Introduction
Swarm
Model
Tenant
AssetClass
Fund
A fund represents a portfolio position, including all entities and properties that are needed to represent the position and compute its metrics.
For example:
- entities may be transactions and prices (via series),
- properties may be classification values, e.g. sector or strategy, some of which may even be historized.
There is a specific implementation of Fund for every asset class type.
Every specific version may have additional properties and even a specific way to implement the computation of a given metric.
Dynamic properties
Some properties are dynamic, meaning that they are not stored in data but computed with a logic that depends on the internal state of the entity (at a given date).
Open/Active
A fund is considered open if its market value is not zero, or if it has no series or no transactions (i.e. a newly create one).
Closed
A fund is closed if is not open.
Inactive
A fund is inactive (in a given period of time [t1,t2]) if it is closed at t2 and open at t1 and has a non-zero PL in the period.
Serie
Transaction
Nav
Custodian
Common metrics
Asset specific metrics
Total Invested
Is the sum of all transactions with direction in this set:
BUY, DRAWDOWN, DEPOSIT_IN, DECREASE_DEBIT, CARRIED_INTEREST_POSITIVE, RECALLABLE, CASHOUT
It is computed from inception to a given date. There is a value in local currency and one in Euro.
Total disinvested
Same logic of Total Invested, but related to directions
SELL, DISTRIBUTION, DEPOSIT_OUT, INCREASE_DEBIT, CASHIN
Amount invested
Also referred to as "Invested at risk".
For quantity based funds
\( q * \overline p \)
where
\( q \) = current quantity
\( \overline p \) = average price
For flow driven funds
\( i - d \)
where
\( i \) = total invested
\( d \) = total disinvested
For Private Equity, Real Estate and Deposit cannot be negative, in case disinvested>invested then is zero by definition.
For Leverage it cannot be positive, in that case is zero by definition.
It is computed at given date. There is a value in local currency and one in Euro.
Private equity metrics
Total Invested
Is the sum of all transactions' amount with directions
\( TOTAL\_INVESTED = \sum DRAWDOWN + \sum CARRIED\_INTEREST\_POSITIVE - \sum RECALLABLE \)
It is computed from inception to a given date.
There is a value in local currency and one in Euro.
Total disinvested
Same logic of Total Invested, but related to distributions.
\( TOTAL\_DISINVESTED = \sum DISTRIBUTION \)
Amount invested
Also referred to as "Invested at risk".
\( AMOUNT\_INVESTED = TOTAL\_INVESTED - TOTAL\_DISINVESTED \)
It cannot be negative, in case disinvested>invested then is zero by definition.
It is computed at given date.
There is a value in local currency and one in Euro: in the computation of the amount in Euro every transaction is converted with its own fx value.
Carried Interest
Is the sum of all transactions' amount with direction CARRIED_INTEREST_POSITIVE or CARRIED_INTEREST_NEGATIVE.
It is computed from inception to a given date.
Deployed Capital
Is the sum of all transactions' amount with direction
\( DEPLOYED\_CAPITAL = \sum DRAWDOWN + \sum COMMISSION + \sum CC\_COMMISSION - \sum RECALLABLE \)
NB: Normal Distributions and Carried Interest are ignored.
It is computed from inception to a given date.
There is a value in local currency and one in Euro: in the computation of the amount in Euro every transaction is converted with its own fx value.
Residual Capital (Uncommitted)
Is the amount of capital still committed, always computed from inception to a given date.
Its formula makes sense only when computed in LC:
\( RESIDUAL\_CAPITAL_{ LC}(date) = COMMITMENT_{LC} - DEPLOYED\_CAPITAL_{LC}(date) \)
There is a value in Euro, simply obtained by dividing the LC amount by the exchange rate at the given date.
\( RESIDUAL\_CAPITAL_{EUR} (date) = RESIDUAL\_CAPITAL_{LC}(date)/FX(date) \)
Therefore please note that:
\( RESIDUAL\_CAPITAL_{EUR} (date) \neq COMMITMENT_{EUR} - DEPLOYEDCAPITAL_{EUR}(date) \)
Capitalized commissions
Total invested BS
BS = Balance Sheet
Markets metrics
All market related asset classes (Stock, Bond and Hedgefunds) share the same set of basic metrics.
Leverage metrics
Assets
SWARM supports a wide range of asset classes. The following is a list of the asset classes supported by SWARM:
Markets
Stocks
Bonds
Investments
Private Equity
Direct Investments
Real Estate
Collectibles (Art)
Cash
Cash assets management includes:
- custodians: accounts for cash retrieval and deposits.
- deposits: time-bound accounts with periodic interest.
- leverage: borrowed cash accounts with periodic negative interest.
- FX/Forex: trading in different currencies.
Custodians
Accounts in which cash funds are freely retrieved (cashout, asset buy or expenses/cost settlements) and deposited (cashin, asset sell or income settlements).
Deposit
Accounts in which cash funds are deposited for an agreed amount of time and not freely retrievable. Interests are paid periodically at an agreed rate.
Leverage
Leverage represents accounts in which cash funds are borrowed for an agreed amount of time (Lombard, Loans, ..).
Negative interests are paid periodically at an agreed rate.
Debit amount may be increased or decreased during investment lifespan.
See Leverage for more information.
LeverageFund
The only additional attribute of a Leverage Fund is the interest rate (%).
LeverageSerie
Although LeverageFunds may have multiple series, e.g. to represent different tranches of a loan, generally only one is specified.
The additional attributes of a Leverage Serie are:
- the maturity date
- the yield (%)
All fund and series attributes are recorded for information purpouse, but are not used in any calculation.
Any metric (borrowed amount, exposure per custodian, etc...) is not specified by the user but computed dynamically from the transactions.
LeverageTransactions
Every Leverage transaction specify the settled amount in the price attribute, the quantity is fixed to 1. As usual also the corresponding custodian and trading/settlement dates are required.
The allowed directions are:
- Increase Debit: the amount is borrowed and added to the debit, the amount is deposited as cash in the custodian
- Decrease Debit: the amount is repaid and subtracted from the debit, the amount is withdrawn as cash from the custodian
- Interest positive: an interest amount is paid off. A positive amount is deposited in the custodian.
- Interest negative: an interest amount must be paid. A negative amount is withdrawn from the custodian.
- Commission: a commission is paid to the custodian.
- Tax: tax is paid to the custodian.
Only increase debit and decrease debit transactions contribute to the total debit amount.
Interests, commissions and taxes have no impact in the total debit amount but contribute to the fund return.
For all metrics details refer to leverage metrics.
FX
Fx (or Forex) refers to the exchange of (a pair of) currencies at an agreed time and exchange rate.
The main concepts in the FX model is the exchange rate between the two currencies, either the market rate or the rate agreed with an intermediary (strike) and used in transactions.
See Forex for more information.
Swarm models FX funds as a pair of currencies (one of them must be Euro) and an amount (notional), always expressed in the currency that is not the Euro.
An FX fund generally contains a large number of series that represent all the different operations in the total position, and its metric represents the whole history of the FX positions.
It is however possible to create a new fund every time a new operation is performed, in this case the fund metrics will refer to a single operation.
Two kinds of operations are implemented in the FX model:
- Spot: The immediate exchange of currencies at an agreed rate (generally the current market rate plus a markup).
- Forward: The exchange of currencies at a future date at a rate agreed today.
The operation also specifies the direction of the exchange, referred to the non-Euro currency, which can be either BUY or SELL.
Both operations are modeled as a pair of transactions, one for each currency, with the same amount and opposite directions.
In case of a spot the trading date and settlement date are the same, while in a forward the settlement date match the series maturity date (or the closing date when an anticipated closing happens).
Swarm FX actions
Swarm users do not handle directly the creation of the FX series or the couple of FX transactions, but they can perform four kinds of actions:
- On a FX Fund:
- New conversion: Create a new FX series of type spot (named CONV) with two transactions representing a spot operation.
- New hedging: Create a new FX series of type forward (named HDG) with two transactions representing an open forward operation.
- On a FX Serie:
- Close: If the series represents a forward operation, the close operation creates two transactions representing a spot of opposite sign in order to realign the custodians. The specified exchange rate is used as the strike of the spot and also saved as the current series fxAtMaturityDate.
- Roll: If the series represents a forward closed operation, the roll adds a nearly identical series (of type forward) starting from the current series maturity/closing date. The specified exchange rate is used as the strike of the new forward series.
During close and roll the default value for the notional is the one of the series being closed/rolled, but it can be overridden with a different value (partial close/renew).
The user must specify the trading and settlement dates, two custodians (one per currency), the notional, the direction of the operation and an exchange rate.
See above explanations on how these parameters are used in series/transactions creation depending on action type.
Anticipated closing
In case of a forward operation, it is possible to close the series before the maturity date, this is called an anticipated closing.
Everything happens as a normal closing, but the closing date is before the maturity date.
Dash
Main selections
There are three main selections that a user must perform:
Tenant
If a user have access to multiple tenants, he can switch from one tenant to the other. Every tenant has its own set of pages.
Page
The user can access one of a set of different pages, representing either the analysis dashboard for a group of positions or some specific reporting pages (e.g. business plan).
Period
The user can specify a given period (time interval) which will be used to compute all the metrics displayed in the page (in charts, lists, etc..). Note that a given metric (and therefore the corresponding chart) can depend on either dates or on only one of them (generally the end date). See metrics for details.
Custom selection
The user can specify manually the begin and end dates of the time period.
Preset periods
The use can specify a predefined rule to automatically set the time period (e.g. This year, Last year, Since inception)
Pages
Portfolio Investments
Details
Details table shows all the metrics computed for individual positions of current page.
Some metrics are common to all types of asset classes, some are specific to a given one.
Positions correspond to funds and are displayed in two different ways:
- if the page contains a single asset class or asset classes of the same kind, then funds are grouped in two main groups based on their status: active and inactive.
- if the page contains asset classes of different kind (e.g. overview) then only active funds are shown and funds are grouped on their asset class
Piggy
Piggy
Open Banking
How to refresh OpenBanking credentials
Da piggy, pagina custodians, nella prima fila di bottoni ce ne è uno che mostra lo stato globale delle configurazioni OpenBanking
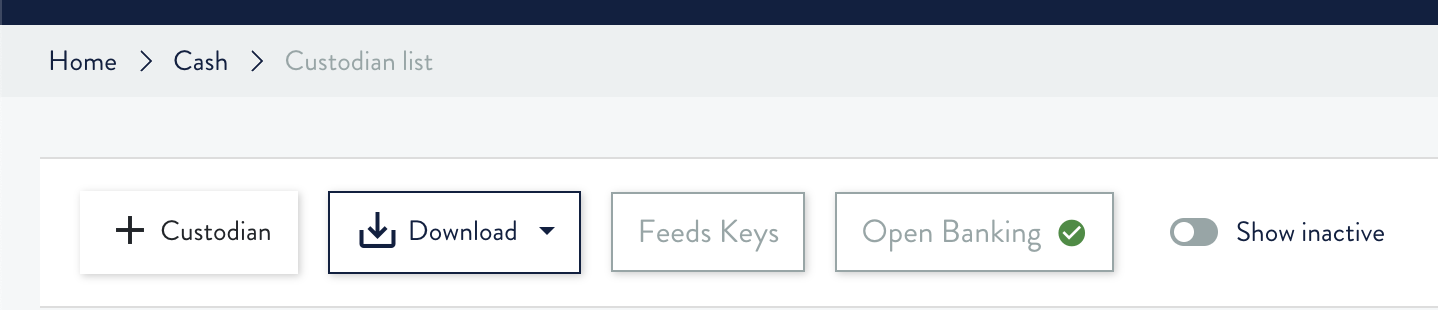
- Se è verde allora tutte le configurati e credenziali sono OK.
- Se è giallo allora almeno una delle credenziali sta per scadere (entro una settimana)
- Se è rosso allora almeno una delle configurazioni non è valida oppure almeno una delle credenziali è scaduta (le credenziali durano 2/3 mesi).
Cliccando sul bottone viene mostrata una legenda

e sulla tabella vengono mostrate delle nuove colonne con lo stato specifico di ogni custodian
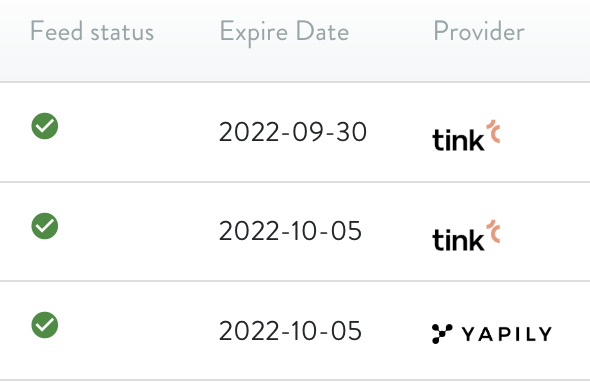
Cliccando sull’icona del Feed Status viene visualizzata la pagina di configurazione OpenBanking specifica
La sezione “Credentials” mostra i dettagli sullo stato delle credenziali e, qualora siano scadute, il bottone per rinnovarle ( ).
Il rinnovo rimanda l’utente sul sito della banca specifica dove dovrà effettuare un login come se stesse accedendo ad una normale sessione di Internet Banking. Ogni banca ha un workflow leggermente differente.
Nel caso di Mediolanum vengono mostrate tre schermate:
- Notifica generale di cosa sta per succedere
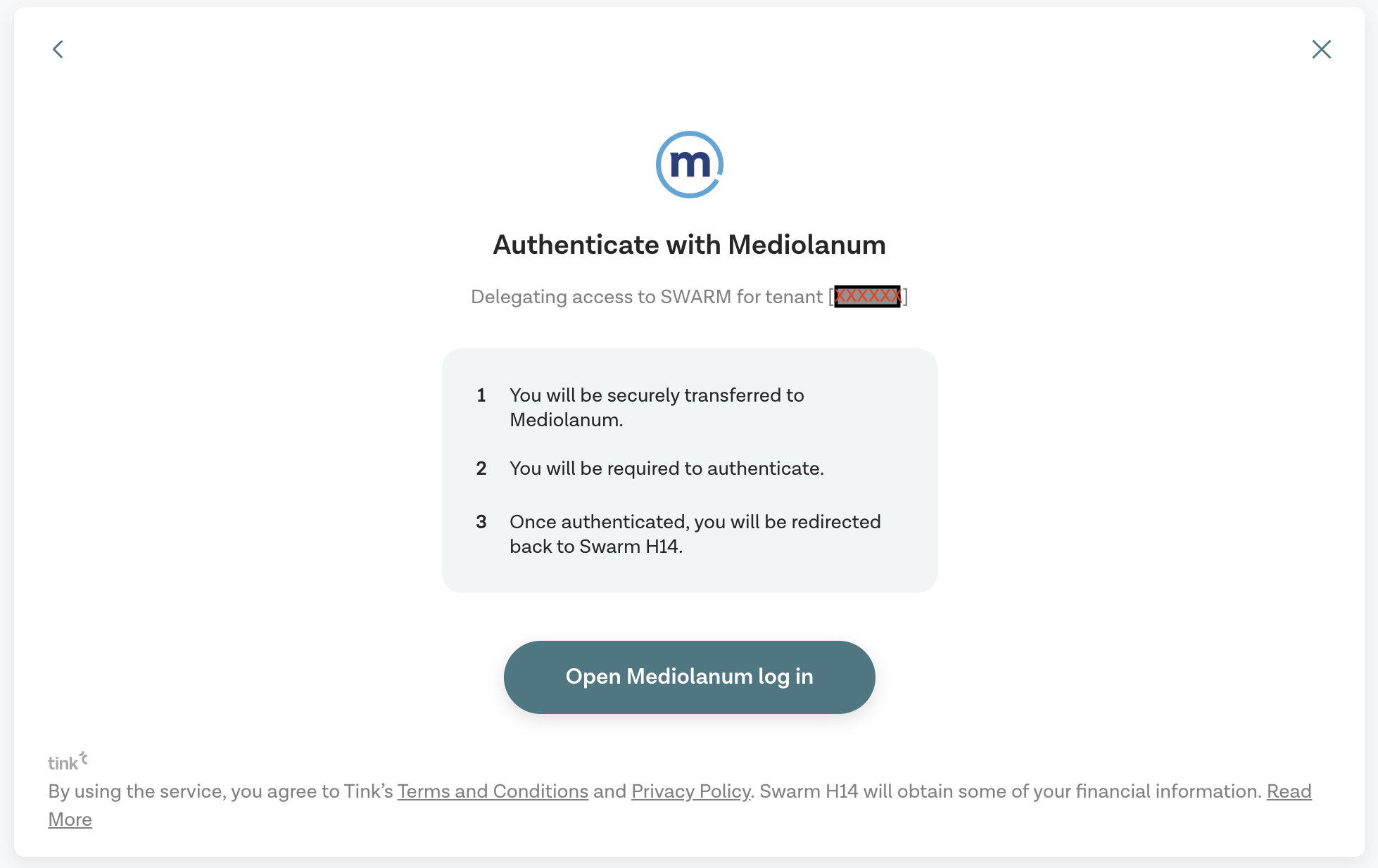
Premere “Open Mediolanum log in”
- Inserimento codice cliente e primo codice segreto
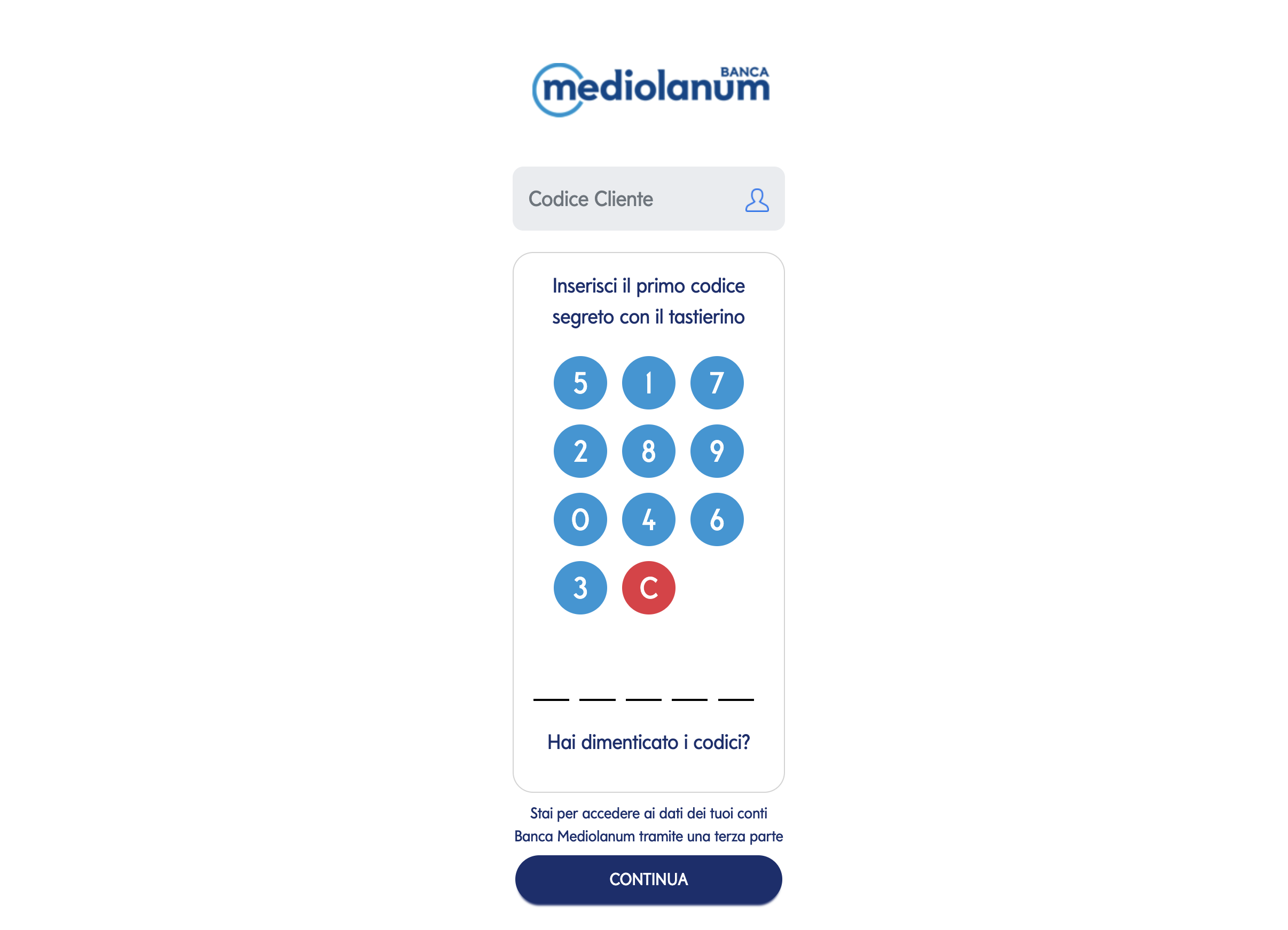
Inserire codice cliente e primo codice segreto (attenzione: il secondo codice segreto non è necessario, serve solo per le operazioni dispositive).
A questo punto possono succedere due cose:
-
sullo smartphone del cliente arriva una richiesta di conferma dell’accesso, e bisogna solo aspettare che il cliente dia conferma.

-
Al cliente viene mandato un codice temporaneo (tramite SMS o come notifica della app Mediolanum) che deve essere inserito nella pagina del browser (simile a quella sopra ma invece del bottone “Conferma dal tuo telefono” compare un campo dove inserire il codice.
La finestra del browser si riapre su Swarm/Piggy e le credenziali sono rinnovare per altri 3 mesi.
Format
MathJax Support
\( \int x dx = \frac{x^2}{2} + C \)
\[ \mu = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=0} x_i \]
Mermaid
graph TD;
A[Luigi All] -->|33.3%| B(H14)
A[Luigi All] -->|100%| L(Luigi Personal)
A[Luigi All] -->|100%| ELH(EL Holding)
A[Luigi All] -->|80%| I1(Ithaca 1)
A[Luigi All] -->|80%| I2(Ithaca 2)
A[Luigi All] -->|80%| I3(Ithaca 3)
BB[Barbara All] -->|33.3%| B(H14)
BB[Barbara All] -->|100%| BBP(Barbara Personal)
EB[Eleonora All] -->|33.3%| B(H14)
EB[Eleonora All] -->|100%| EBP(Eleonora Personal)